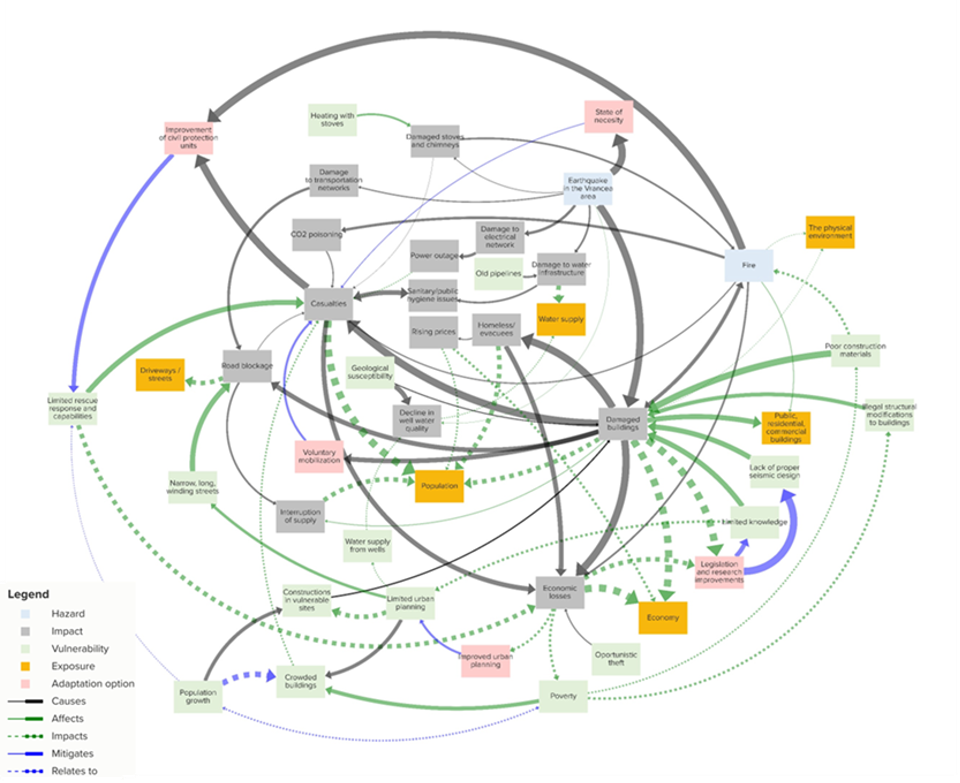
Figure 1: Complex Interaction of historical events 1940 to 1970 in Bucharest
Iqra Naz, University of Twente
Disasters are becoming increasingly complex, with devastating impacts on communities. Understanding the complexity of disasters is crucial in building resilience to future events. Disasters are not single events. They are processes with multiple triggering points, causes, and direct and indirect impacts. Accurate information and an inclusive understanding of the multi-hazards risk assessment and direct and indirect impacts of these events are crucial in mitigating their effects. By understanding the true impact of these disasters, policymakers and community leaders can make informed decisions to mitigate future risks, allocate resources effectively, and develop resilience strategies. Having reliable data on the indirect effects of disasters can also aid in securing funding and support from external sources, such as governments and non-profit organizations, to assist affected communities in their recovery and rebuilding efforts. Therefore, investing in research and developing inclusive frameworks for measuring these indirect effects is crucial for ensuring the long-term sustainability and well-being of communities facing the challenges of climate change and disaster resilience. Additionally, it also can help identify the most vulnerable communities and prioritize their needs in disaster preparedness planning. This can involve assessing factors such as socio-economic status, infrastructure quality, and access to healthcare, to ensure that resources are distributed equitably and effectively.
“We cannot stop natural disasters but can arm ourselves with knowledge: so, many lives wouldn’t have to be lost of there was enough disaster preparedness” – Petra Nemcova
A disaster-WIKI acts as a digital repository using historical data and forensic analysis of past hazards to provide valuable insights for disaster preparedness and planning. PARATUS will develop a WIKI with standardized impact chains to analyse how the hazardous event impacted different sectors, such as society, human health, cultural heritage, environment and biodiversity, public finance, and key economic sectors in its learning and application case studies. The WIKI is based on the analysis of the relational impact chain of vulnerability and risk (the interconnected relationship between different factors that contribute to the vulnerability of a community to hazards). The development process of this tool will include reports, interviews with specific stakeholders, testimonies, videos, virtual workshops for learning cases and presence meetings for application cases.
Understanding the complex web of hazards interaction makes it challenging to predict the impact of a specific event accurately. Building resilience in the face of disasters requires a collaborative assembly of researchers, decision-makers, and the global community. The disaster wiki would also serve as a platform for knowledge sharing and a digital brainstorming session where different stakeholders collectively work to complete the puzzle of disasters. The disaster wiki would be accessible to the global community, enabling people from different backgrounds to share their experiences and data. This knowledge sharing helps us understand the local impact of disasters and develop strategies to build resilience at the community level. Data-driven decision-making ensures readiness and a well-informed response to disasters, while collective expertise provides a complete understanding of hazards.
Predicting future impacts is challenging due to the dynamic nature of systemic risk and changing societal, economic, and environmental conditions. The disaster wiki can assist in predicting future impacts and enhancing our ability to plan for and respond to disasters. By aggregating and analyzing data from past disasters, the disaster wiki can identify patterns and trends that help in predicting future impacts. This knowledge can then be used to inform the development of effective strategies and policies to mitigate risks and enhance resilience. Additionally, the disaster wiki can serve as a platform for sharing best practices and lessons learned, facilitating collaboration and knowledge exchange among communities facing similar challenges.
| Relevant Keywords | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Multi-hazards risk assessment | An evaluation of multiple hazards that can impact a given area, including natural and human-induced disasters. |
| Direct and indirect impacts | The immediate and lasting effects of a disaster event on communities, infrastructure, and the environment. |
| Wiki | A digital platform that allows for collective information sharing and collaborative knowledge building. |
| Resilience | The ability of a community to prepare for and recover from a disaster event, building back better and stronger. |
| Readiness | The state of being prepared to face a disaster event, with appropriate planning, resources, and training in place. |